Excitement About Medicare Advantage Agent
Table of ContentsThe Facts About Medicare Advantage Agent UncoveredSome Ideas on Medicare Advantage Agent You Need To KnowWhat Does Medicare Advantage Agent Mean?
follows from perplexing the reasonably young age profile of the uninsured with the far better health and wellness, usually, of more youthful persons. This covers the web link in between health status and medical insurance. For those without accessibility to work environment medical insurance, inadequate health is a possible barrier to buying nongroup coverage due to the fact that such protection may be extremely valued, leave out pre-existing problems, or be just inaccessible. The number of without insurance Americans is not specifically huge and has not transformed in current years. Seven out of 10 participants in a nationally representative survey thought that less Americans lacked health and wellness insurance coverage than really do(Fronstin, 1998). Approximately fifty percent(47 percent )thought that the number of people without medical insurance lowered or continued to be consistent over the latter fifty percent of the last years(Blendon et al., 1999). This drop of almost 2 million in the number of people 'without insurance coverage (a reduction
of about 4 percent)is definitely a favorable adjustment. With a softer economic situation in 2000 the most up to date reported gains in insurance protection might not proceed(Fronstin, 2001 ). The decrease in the variety of without insurance will certainly not proceed if the economic situation continues to be sluggish and healthcare prices remain to surpass rising cost of living. This is because the data were gathered for a duration of solid financial performance. Of the estimated 42 million individuals that were uninsured, just about regarding 420,000(regarding 1 percent)were under 65 years of age, the age at which most Americans end up being eligible for Medicare; 32 million were adults between ages 18 and 65, around 19 percent of all grownups in this age group; and 10 million were kids under 18 years old, regarding 13.9 percent of all kids (Mills, 2000). These quotes of the number of persons uninsured are generated from the annual March Supplement to the Existing Populace Study (CPS), conducted by the Census Bureau. Unless otherwise kept in mind, nationwide quotes of people without health insurance and percentages of the population with different kinds of coverage are based upon the CPS, one of the most extensively used source of estimates of insurance policy protection and uninsurance prices. These surveys and the quotes they generate are explained briefly in Table B. 1 in Appendix B - Medicare Advantage Agent. These surveys vary in size and tasting techniques, the questions that are asked concerning insurance coverage
More About Medicare Advantage Agent
protection, and the moment duration over which insurance policy protection or uninsurance is measured(Lewis et al., 1998, Fronstin, 2000a ). Still, the CPS is particularly useful since it produces annual quotes fairly swiftly, reporting the previous year's insurance coverage approximates each September, and due to the fact that it is the basis for a constant collection of price quotes for more than twenty years, permitting for analysis of trends in protection gradually.

The Definitive Guide for Medicare Advantage Agent
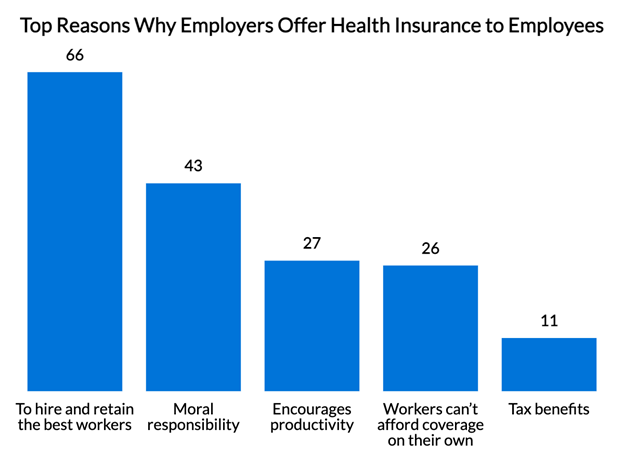
Over a three-year period starting early in 1993, 72 million people, 29 percent of the united state population, lacked coverage for at the very least one month. Within a single year(1994), 53 million people experienced at the very least a month without coverage(Bennefield, 1998a). 6 out of every 10 uninsured grownups are themselves used. Although working does boost the probability that one and one's member of the family will have insurance policy, it is not an assurance. Even members of family members with two full-time breadwinner have practically a one-in-ten possibility of being without insurance (9.1 percent uninsured price)(Hoffman and Pohl, 2000 ). The partnership between wellness insurance and access to care is well developed, as recorded later in this chapter. Although the connection in between health and wellness insurance and health and wellness outcomes is neither straight nor easy, a considerable medical and health and wellness solutions study literary works links health insurance protection
to enhanced accessibility to care, far better top quality, and improved personal and populace wellness status. The second record, on individual health outcomes for without insurance grownups, is represented by the inner circle of the figure, while the third record, on household go health, encompasses the subjects of the 2nd record however emphasizes a different unit of evaluation, namely, the family. The sixth record in the series will offer info regarding approaches and efforts undertaken locally, statewide, or nationally to attend to the absence of insurance coverage and its damaging effects. Levels of evaluation for taking a look at the effects of uninsurance. This conversation of medical insurance coverage concentrates mainly on the united state population under age 65 due to the fact that practically all Americans 65 and older have Medicare or various other public protection.
It concentrates especially on those without any type of health and wellness insurance coverage for any length of time. The problems encountered by the underinsured remain in some aspects similar to those dealt with by the uninsured, although they are normally less severe. Uninsurance and underinsurance, however, involve noticeably various policy issues, and the techniques for addressing them may vary. Throughout this research and the 5 reports to comply with, the primary emphasis gets on persons without any medical insurance and hence no support in paying for wellness treatment beyond what is available via charity and safeguard establishments. Medical insurance is a powerful factor influencing invoice of care because both people and medical professionals react to the out-of-pocket rate of solutions. Medical insurance, nonetheless, is neither needed nor enough to acquire access to clinical services. However, the independent and direct effect of health and wellness
insurance protection on access to wellness services is well developed. Others will obtain the wellness treatment they need also without medical insurance, by paying for it expense or seeking it from carriers that supply care totally free or at very subsidized prices. For still others, health and wellness insurance alone does not ensure invoice of treatment due to other nonfinancial barriers, such as a lack of healthcare providers in their neighborhood, minimal access to transport, illiteracy, or etymological and cultural differences. Official study about without insurance populaces in the United States dates to the late 1920s and early 1930s when the Board on the Price of Medical Care produced a collection of reports regarding funding medical professional office gos to and hospital stays. This issue ended up being significant as the numbers of medically indigent climbed during the Great Clinical depression. Empirical researches consistently support the link between access to care and enhanced health and wellness results(Bindman et al., 1995; Starfield, 1995 ). Having a normal resource of treatment can be taken into consideration a forecaster of accessibility, instead of a direct step of it, when wellness end results are themselves made use of as accessibility indicators. This extension of the notion of gain access to dimension was made by the IOM Board on Checking Accessibility to Personal Healthcare Provider(Millman, 1993, p. Whether or not parents are insured appears to affect whether their youngsters obtain treatment in addition to just how much careeven if the children themselves have coverage(Hanson, 1998). The wellness of moms and dads can impact their capability to take care of their children and the degree of household anxiety. Stressing concerning their youngsters's accessibility to care is itself a resource of anxiety for moms and dads. 3 chapters follow in this record. Phase 2 offers a summary of how employment-based wellness insurance policy, public programs and private insurance coverage run and communicate to provide comprehensive but insufficient insurance coverage of the U.S. populace. This consists of a testimonial of historical trends and public laws impacting both public and private insurance policy, a conversation of the interactions among the different kinds of insurance, and an examination of why individuals move from one program to one more or end up